Neutralization of NaAlO2 solution with CO2 for synthesis of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles, part 1: effects of synthesis parameters in semi-batch membrane dispersion microstructured reactor
Abstract
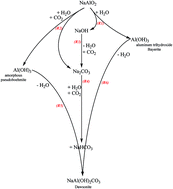
Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 is the most important alumina structure directly applicable as a chemical and petrochemical catalyst support. Textural, chemical and physical properties of the support dramatically affect the catalyst performance. Pseudoboehmite is a precursor for γ-Al2O3 and a novel simple, one-pot, solvent-deficient method is used as the synthesis route, which involves the reaction of micro bubbled CO2 gas with NaAlO2 aqueous solution. The support's characteristics including pore size, surface area, pore volume, thermal stability and acidity could be controlled by the preparation parameters. However there is still no known comprehensive study on this single stage, simple, fast, promising synthesis path. The literature describes several techniques for alumina synthesis. Since this method is newly developed, extensive research has not been undertaken in this field. To fill the knowledge gap, a comprehensive study of preparation parameter effects on pseudoboehmite properties was performed. Pseudoboehmite was synthesized using a semi-batch membrane dispersion microstructured reactor. The effects of gas flow rate, CO2 concentration in the gas stream and type of inert gas, aging temperature and time, concentration of NaAlO2 in aqueous solution, synthesis temperature and final pH of the parent solution were studied. Pure pseudoboehmite could be obtained through this synthesis route based on XRD results. Screening results revealed that BET surface area and average pore size could be controlled by some of the synthesis parameters independently of pore volume. Maximum BET surface area, average pore size and pore volume of pseudoboehmite were about 365 m2 g−1, 155 Å and 1.08 cm3 g−1 respectively. This pseudoboehmite synthesis route could be introduced as a simple practical alternative method, due to simplicity, good repeatability of the synthesis procedure and acceptable controllability of pore size, pore volume and surface area of the obtained catalyst support precursor based on XRD, BET and SEM results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...