Ultrasmall SnS nanoparticles embedded in carbon spheres: a high-performance anode material for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
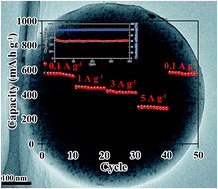
In this article, we report on the preparation of ultrasmall SnS nanoparticles embedded in carbon spheres (called SnS/C nanocomposite) by one pot aerosol spray pyrolysis and its application as a high-rate and long-cycle life anode material for sodium-ion batteries. The structure and morphology analysis of the as-prepared nanocomposite shows that SnS nanoparticles with a size about 5 nm are homogeneously dispersed in the carbon spheres (denoted as 5-SnS/C). The sizes and components of SnS particles can be controlled by adjusting the precursor's concentration. When applied as an anode material of sodium-ion batteries, the 5-SnS/C nanocomposite delivers an initial charge capacity of 560.8 mA h g−1 at 1 A g−1 and maintains a reversible capacity of 517.6 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles at 1 A g−1. In particular, the 5-SnS/C electrode exhibits a high-rate capability, with reversible capacities of 428.5 mA h g−1 at 3 A g−1 and 315.4 mA h g−1 at 5 A g−1, respectively. The excellent electrochemical performance of 5-SnS/C is due to the fact that the uniformly embedded ∼5 nm SnS nanoparticles in the stable carbon matrix can alleviate the volume expansion during cycling with a buffering effect to prevent aggregation of SnS nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...