A visible light mediated synergistic catalyst for effective inactivation of E. coli and degradation of azo dye Direct Red-22 with mechanism investigation†
Abstract
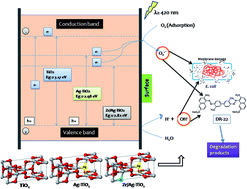
Novel zirconium and silver co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles were fabricated and utilized as effective multifunctional visible light photocatalysts for inactivation of bacteria (E. coli) as well as degradation of dye pollutant (Direct Red-22) for the first time. Results revealed co-doping of Ag and Zr in the lattice of TiO2 could remarkably narrow the band gap (2.82 eV) indicated by UV-Vis and photoluminescence studies. The degradation pathway for Direct Red-22 (50 mg L−1) proposed using LC-MS, reveals the breaking of the dye into low-toxic metabolites after 5 h. The bactericidal effect against E. coli was found to be high for Zr/Ag–TiO2 (100% inhibition) compared to Ag–TiO2 (74% inhibition) and Zr–TiO2 (48% inhibition), which was further supported by TEM and K+ release assay (3.21, 2.34 and 1.62 ppm of K+ for Zr/Ag–TiO2, Ag–TiO2 and Zr–TiO2, respectively). DNA analysis indicated no fragmentation during inactivation. Detailed analysis of the reaction mechanism was performed by active species (˙OH and O2˙−) trapping experiments, NBT transformation and terephthalic acid-photoluminescence probing technique (TA-PL). The activity is found to correlate with the concentration of radicals and is found to be maximum for Zr/Ag–TiO2. This work is expected to provide new insights into multifunctional nanomaterials for applications in solar photocatalytic degradation of harmful organics and common pathogenic bacteria in wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...