Milk glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and glucose-6-phosphate are associated with oxidative stress and serve as indicators of energy balance in dairy cows
Abstract
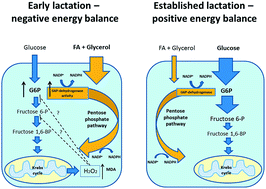
Early lactation in high-producing dairy cows is associated with negative energy balance (EB) and with massive lipolysis to support the energy demands for milk production. The large influx of free fatty acids and glycerol increases oxidative stress in the mammary gland. Milk concentrations of glucose and glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), level of the oxidative stress marker malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity of milk, calculated EB and various parameters reflecting EB (plasma concentrations of nonesterified fatty acids and body condition score), and glucose metabolism (plasma insulin concentration) were measured in 12 high-yielding dairy cows in early lactation (3–57 days in lactation), once a week for 4 weeks. Weekly averages of milk glucose concentration increased from 81 to 184 μM, and of milk G6P decreased from 223 to 81 μM. The activity of milk G6PDH decreased from 902.8 to 256.4 mU ml−1, so that the G6P/glucose ratio in milk decreased from 3.5 to 0.5. A significant correlation between milk G6PDH activity and milk G6P concentration, and an inverse relationship between milk MDA concentration and days in lactation suggest that G6P is shunted to the pentose phosphate pathway in the mammary gland in early lactation, as part of a homeostatic adaptation to counterbalance the excess oxidative stress during early lactation in dairy cows. Milk G6P concentration and G6P/glucose ratio may serve as objective, accurate and noninvasive indicators of EB in dairy cows and potentially in other mammals subjected to negative EB and oxidative stress.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...