Induction of intrinsic apoptotic pathway and cell cycle arrest via baicalein loaded iron oxide nanoparticles as a competent nano-mediated system for triple negative breast cancer therapy
Abstract
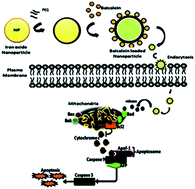
Magnetic nanoparticles have shown an increasing number of applications in the field of molecular medicine. In the present study we investigated the controlled synthesis of biocompatible polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3) loaded with baicalein and evaluated these for their drug loading and release behaviour. Moreover, the loaded particles were evaluated for their anti-proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis activation properties in triple negative breast cancer cells. The structure, morphology and magnetic properties of the prepared materials were studied by using scanning electronic microscopy, transmission electronic microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, dynamic light scattering analysis and zeta potential analysis. DLS and TEM analysis confirms that the size of the synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles are about 90–100 nm and that they are extremely crystalline and spherical in nature. FTIR analysis confirms that the baicalein molecules were conjugated with PEG-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction patterns indicate that the magnetic nanoparticles were highly pure with a spinel structure. Baicalein loaded nanoparticles show a controlled release profile in response to various pH levels. We found significant cell cycle arrest at various phases in the treated group and subsequent apoptotic cell death to be evidenced by AO/EtBr, DAPI and PI of fluorescence microscopy analysis. The TUNEL assay evidences that DNA damage occurs in the treated cells. Further baicalein loaded iron oxide nanoparticles exhibit significant down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and up-regulation of pro-apoptotic proteins evidenced by Western blotting. Our findings clearly demonstrate that baicalein loaded iron oxide nanoparticles could efficiently deliver the drug of interest, and initiate and execute the apoptotic process in triple negative breast cancer cells. This could open a new window in polymer surface chemistry to develop metal oxide based drug delivery systems for all kinds of cancer therapeutics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...