Engineering aggregation-induced SERS-active porous Au@ZnS multi-yolk–shell structures for visualization of guest species loading†
Abstract
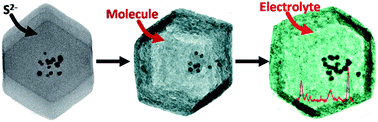
Herein, we present aggregation-induced surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active hierarchical structures that effectively capture guest species loading in hollow nanocaged materials. The developed SERS-active probe by in situ aggregation was constructed of porous Au@ZnS multi-yolk–shell structures derived from Au@ZIF-8 multi-core–shell structure precursors. The porous ZnS shells characterized by nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm enable guest species such as hydrophobic 4-MBA and hydrophilic R6G molecules to shuttle based on their size. As a result of effective localization of the electric field by engineering hotspots in metallic aggregates, the intensity of these SERS reporter molecules adsorbed on Au NPs exhibited a dramatic enhancement during aggregation of Au NPs induced by electrolyte. Although the aggregation of Au NPs was able to be characterized by TEM and the change of plasmonic band from UV-vis absorption, some guest species that were incapable of inducing assembly of Au NPs were difficult to identify by both techniques. After taking into consideration other factors, including the sequence of guest species and incubation time, the variation of SERS signals related to individual Au NPs and their aggregates was applied to visualization of different types of molecules with Raman activity and ion loading in porous nanocages.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...