Selective removal of isoquinoline and quinoline from simulated fuel using 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-diol (BINOL): crystal structure and evaluation of the adduct electronic properties†
Abstract
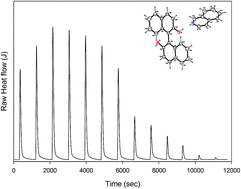
1,1′-Binaphthyl-2,2′-diol/quinoline (BINOL/QUN) and 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-diol/isoquinoline (BINOL/ISOQUN) adducts were successfully synthesized. X-ray single crystals of BINOL/QUN and BINOL/ISOQUN were grown and analysed. The crystal packing of the molecules in both adducts confirmed that they are held in aggregates by strong hydrogen bonds (O2–H2⋯O3), (O3–H3⋯N1), (O2–H2⋯O1), (O1–H1⋯N1), (O2–H2⋯O1) and weak hydrogen C–H⋯π bonds. The patterns of the hydrogen bonding network as well as the conformation of BINOL contribute to the formation of the shape of the voids that entrap quinoline and isoquinoline. Molecular modelling which was employed to investigate the electronic properties of BINOL/QUN and BINOL/ISOQUN shows that the HOMO positions of the adducts are localized around the 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-diol (BINOL), while the LUMO is positioned on isoquinoline and quinoline. Thermodynamic parameters obtained from isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) revealed a stronger isoquinoline/BINOL interaction compared to quinoline/BINOL. 6-Vinyl-1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-diol was co-polymerized with styrene to form [DBN-co-STY]. Electrospun [DBN-co-STY] exhibited selectivity for quinoline and isoquinoline in a model simulated fuel presenting an adsorption capacity of 2.2 and 2.4 mg g−1 respectively. The adsorption study showed a higher adsorption capacity for isoquinoline compared to quinoline. This may be attributed to the more favourable electronic properties (HOMO–LUMO properties) of isoquinoline. This concept demonstrates the possibility of extracting/separating isoquinoline and quinoline from fuel.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...