Solution synthesis of pure 2H CuFeO2 at low temperatures†
Abstract
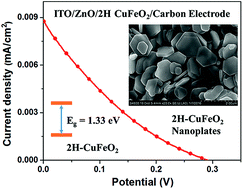
Pure 2H CuFeO2 nanoplates with a thickness of about 100 nm were synthesized at temperatures as low as 100 °C from CuI and FeCl3·6H2O. Systematic studies revealed that the formation of 2H CuFeO2 was affected by reactant concentrations, basicity, temperature and the reaction time. The material was characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, Raman and absorption spectroscopy. 2H CuFeO2 has a band gap of 1.33 eV, high absorption coefficient of 3.8 × 104 cm−1 at 700 nm and is highly photostable. When incorporated into an indium tin oxide/ZnO/2H CuFeO2/graphite/carbon black structure an open circuit photovoltage of 0.29 V was observed. The material appears promising for solar applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...