Chiral polyoxomolybdate-based hybrid compounds obtained by spontaneous resolution: syntheses, structures and non-linear optical properties†
Abstract
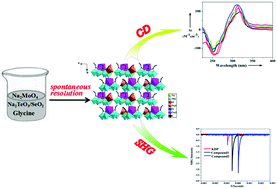
In this study, we report two chiral sheet-like structures based on amino acid functionalized polyoxomolybdates, [Na(H2O)2][Na(H2O)3][MMo6O21(O2CCH2NH3)3]·2.5H2O (M = Te 1 and Se 2; O2CCH2NH3 = glycine), which were synthesized by spontaneous resolution without a chiral auxiliary. They were characterized using single crystal X-ray crystallography, elemental analysis, powder X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy, solid diffuse reflective spectrum, circular dichroism spectrum and TG analysis. The isostructural compounds 1 and 2 crystallize in the chiral space group P21 and exhibit a 2D chiral framework in which glycine functionalized polyoxoanions [MMo6O21(O2CCH2NH3)3]2− as structural units are linked together by the alkali metal Na+ cations. According to the chiral structure of both compounds, we speculate that the symmetry breaking of the polyoxoanions mainly depends on attaching glycine and Na+ cation to the polyoxometalates by covalent bonds. The absolute configuration of 1 and 2 was determined from the Flack parameter using X-ray crystallography and solid state circular dichroism spectroscopy. Remarkably, the bulk sample has an enantiomeric excess, confirmed by the random measurement of 8 single crystal data of compound 1 and the solid state circular dichroism spectra of bulk sample 1. Furthermore, in consideration of the asymmetric structure, we detected the second harmonic generation (SHG) efficiency of both compounds, which respectively show an SHG response of approximately 3.5 and 3.7 × KH2PO4. To the best of our knowledge, compounds 1 and 2 represent the chiral heteropolymolybdates holding the strongest SHG efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...