Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of UV-emitting carbon dots from tannic acid†
Abstract
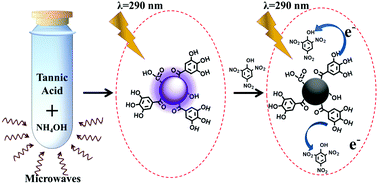
We report herein an easy, facile, economic and solution-based synthesis protocol for UV-photoluminescent carbon dots (CDs) using tannic acid, an environmentally benign, in-expensive and readily available precursor, following a microwave-assisted hydrothermal route. The as-synthesized CDs exhibited excellent aqueous solubility and displayed excitation-wavelength independent emission at 370 nm. The CDs were explored for highly selective and extremely sensitive detection of picric acid in aqueous media exploiting luminescence quenching. The detection limit of the as-synthesized CDs towards picric acid was about 0.6 pM, and the linear range extends from 0 to 10 nM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...