Photo-extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Baker's yeast and their anticancer evaluation against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells
Abstract
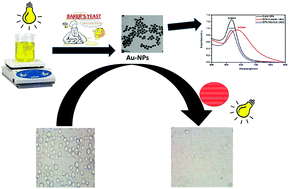
The chemical methods for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles lead to the formation of some toxic chemicals adsorbed on the surface that may have adverse effects on their medical applications. Hence, the need to develop environmentally benign nanoparticles has attracted growing interest. Gold nanoparticles with 13.0 ± 0.9 nm size have been biosynthesized using an aqueous extract of Baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) under visible light. The existing components in the aqueous yeast extract were identified for the first time as trimethylsilyl derivatives of butan-2,3-diol, glucose, indole-3-acetic acid and undecanoic acid. This extract acts as a capping and reducing agent for gold nanoparticles. The cytotoxicity of the biosynthesized gold nanoparticles, chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles of ∼5.0 ± 2.0 nm size and aqueous extract of Baker's yeast towards Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cancer cells has been studied using the Trypan blue exclusion method. The results show that the killed percentage of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells under dark incubation with an aqueous extract of Baker's yeast, chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles and the photo-biosynthesized gold nanoparticles are 9.7%, 12.5% and 24.6%, respectively. These percentages are increased to 10.63%, 60.6% and 86.5% under visible light incubation, respectively. The killing enhancement of the Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells under visible light incubation is proposed based on the photothermal properties of the formed plasmonic gold nanoparticles that conjugated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies beside the phagocytosis of the excess yeast extract that is present in the photo-extracellular synthesized gold nanoparticles sample. The combination between two different treatment ways can give a third one with high affinity for the treatment of cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...