Design and synthesis of DNA-encoded libraries based on a benzodiazepine and a pyrazolopyrimidine scaffold†‡
Abstract
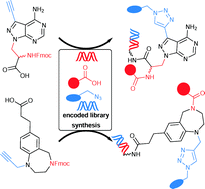
Selection-based screening of large DNA-encoded libraries of drug-like small molecules is a validated method to identify bioactive compounds. Among the chemical space of bioactive compounds certain scaffold structures are well represented. These are commonly called “privileged scaffolds”. We have synthesized DNA-encoded libraries based on two representatives of these scaffolds, a benzodiazepine and a pyrazolopyrimidine, and additionally a third library based on propargyl glycine. All three core structures possess a carboxylic acid to couple them to aminolinker-modified DNA. For subsequent library synthesis they contained an amino function to which a set of carboxylic acid building blocks were coupled, and a terminal alkyne that was reacted with a set of azides to furnish triazoles. The two sets of building blocks, 114 carboxylic acids and 104 azides, were selected with the help of chemoinformatic methods in order to control the physicochemical properties of the final libraries, remove unwanted substructures, and maximize diversity. The set of building blocks contained desthiobiotin allowing for validation of library synthesis. The DNA-encoded libraries were synthesized by split-and-pool combinatorial chemistry yielding three libraries that contain 28.254 compounds together. For DNA barcoding, 5′-phosphorylated double-stranded coding DNA sequences with four base overhangs were ligated with T4 ligase. The resulting DNA-encoded libraries were compared to bioactivity databases and, though being based on core structures well-established in medicinal chemistry, showed novelty with respect to the known bioactive chemical space.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...