Abstract
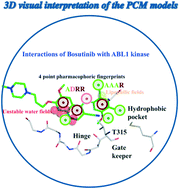
Proteochemometrics, a method that simultaneously uses protein and ligand description, was used to model the target-ligand interaction space of 95 kinases and 1572 inhibitors. To build models, we applied 3-dimensional field-based description of the receptors, which allows the visualization of receptor and ligand features relevant for activity within the spatial framework of the binding sites. Receptor fields were derived from knowledge-based potentials and Schrödinger's WaterMaps, while ligands were described by different 1D, 2D and 3D descriptors. Besides good interpretability, which is important for inhibitor design, the obtained proteochemometric models also predicted external test sets with active and inactive ligands or additional protein targets for ligands with more than 80% accuracy and AUCs above 0.8.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...