Downstream integration of microalgae harvesting and cell disruption by means of cationic surfactant-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles†
Abstract
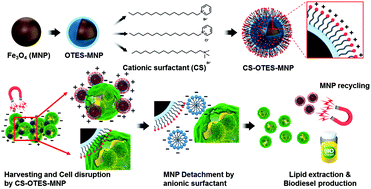
Microalgal biofuel, albeit an exciting potential fossil-fuel-replacement candidate, still requires the development of more advanced downstream processing technology for its price competitiveness. The major challenge in a microalgae-based biorefinery is the efficient separation of microalgae from low-concentration culture broth. The post-harvesting cell-disruption step necessary to render microalgae suitable for lipid extraction, moreover, further raises energy consumption and cost. For the mitigation of biorefinery complexity and costs, we suggest herein a new scheme that integrates the critical downstream processes (harvesting and cell disruption) by means of cationic surfactant-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The cationic surfactants’ quaternary ammonium heads play an important role in not only flocculating negatively charged microalgae but also weakening thick cell walls. In the present study, the harvesting efficiency and cell-damaging effects of three cationic surfactants — cetrimonium bromide (CTAB), cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC), and cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) — were evaluated. The CTAB-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles, which were found to be the most effective, achieved a 96.6% microalgae harvesting efficiency at a dosage of 0.46 g particle per g cell. Next, for the purposes of magnetic nanoparticle recycling and high-purity microalgal biomass obtainment, microalgae detachment from microalgae-Fe3O4 flocs was performed by addition of an anionic surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). The detached CTAB-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles showed a steady reuse efficiency of about 80%. Furthermore, microalgae harvesting by CTAB-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles could contribute to a great improvement in the total extracted lipid content and greener wet extraction without the additional energy-intensive cell-disruption step, thus demonstrating the cell-disruption ability of CTAB-decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...