Citrus flavanones prevent systemic inflammation and ameliorate oxidative stress in C57BL/6J mice fed high-fat diet
Abstract
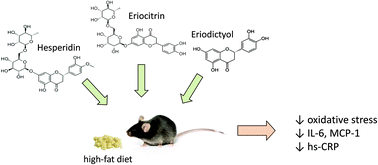
The flavanones hesperidin, eriocitrin and eriodictyol were investigated for their prevention of the oxidative stress and systemic inflammation caused by high-fat diet in C57BL/6J mice. The mice received a standard diet (9.5% kcal from fat), high-fat diet (45% kcal from fat) or high-fat diet supplemented with hesperidin, eriocitrin or eriodictyol for a period of four weeks. Hesperidin, eriocitrin and eriodictyol increased the serum total antioxidant capacity, and restrained the elevation of interleukin-6 (IL-6), macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). In addition, the liver TBARS levels and spleen mass (g per kg body weight) were lower for the flavanone-treated mice than in the unsupplemented mice. Eriocitrin and eriodictyol reduced TBARS levels in the blood serum, and hesperidin and eriodictyol also reduced fat accumulation and liver damage. The results showed that hesperidin, eriocitrin and eriodictyol had protective effects against inflammation and oxidative stress caused by high-fat diet in mice, and may therefore prevent metabolic alterations associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases in other animals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...