Transition metal carbides as novel materials for CO2 capture, storage, and activation†
Abstract
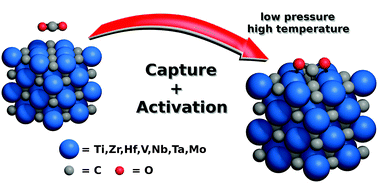
The capture and activation of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) is a prerequisite to its catalytic reforming or breakdown. Here we report, by means of density functional theory calculations including dispersive forces, that transition metal carbides (TMC; TM = Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo) are able to uptake and activate CO2 on their most-stable (001) surfaces with considerable adsorption strength. Estimations of adsorption and desorption rates predict a capture of CO2 at ambient temperature and even low partial pressures, suggesting TMCs as potential materials for CO2 abatement.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...