Polymer versus phosphine stabilized Rh nanoparticles as components of supported catalysts: implication in the hydrogenation of cyclohexene model molecule†
Abstract
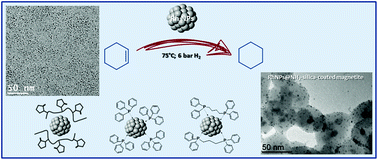
The solution synthesis of rhodium nanoparticles (Rh NPs) was achieved from the organometallic complex [Rh(η3-C3H5)3] under mild reaction conditions in the presence of a polymer (PVP), a monophosphine (PPh3) and a diphosphine (dppb) as a stabilizer, leading to very small Rh NPs of 2.2, 1.3 and 1.7 nm mean size, with PVP, PPh3 and dppb, respectively. The surface properties of these nanoparticles were compared using a model catalysis reaction namely, hydrogenation of cyclohexene, first under colloidal conditions and then under supported conditions after their immobilization onto an amino functionalized silica-coated magnetite support. PVP-stabilized Rh NPs were the most active catalyst whatever the catalytic conditions as a result of a strong coordination of the phosphine ligands at the metal surface that blocks some surface atoms even after several recycles of the supported nanocatalysts and limit the reactivity of the metallic surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...