Elucidating the promotional effects of niobia on SnO2 for CO oxidation: developing an XRD extrapolation method to measure the lattice capacity of solid solutions†
Abstract
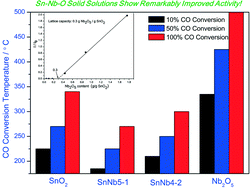
A series of Sn–Nb binary catalysts have been prepared by using a co-precipitation method and used for CO oxidation. All the catalysts show much higher specific surface areas than the individual oxides, indicating their improved thermal stability. It was found that Nb5+ cations can be doped into the lattice of tetragonal rutile SnO2 to replace a portion of the Sn4+ to form a solid solution structure. Using an XRD extrapolation method, the SnO2 lattice capacity for Nb2O5 has been quantified, which proves that only 25% of the Sn4+ in the SnO2 lattice can be replaced by Nb5+ to form a stable solid solution. For the samples with Nb contents below the capacity, the formed solid solution structure can induce the formation of a large quantity of stable and active surface deficient oxygen species due to charge imbalance and lattice defects, which improve the CO oxidation activity remarkably. For the samples with Nb contents above the capacity, the excess Nb is present as free Nb2O5 in the catalysts, which is harmful to their activity. It is concluded that Nb, as an effective promoter for SnO2, must be incorporated into its lattice as Nb5+ to form a solid solution. A Sn–Nb solid solution without excess Nb2O5 is not only a promising catalyst itself, but also a good support for precious metals to prepare catalysts for CO oxidation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...