Kinetic analysis of aqueous-phase cyclodehydration of 1,4-butanediol and erythritol over a layered niobium molybdate solid acid†
Abstract
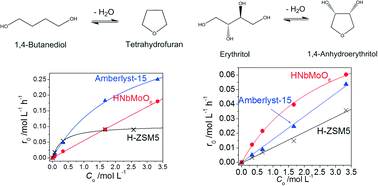
Aqueous-phase reactions are desirable for the transformation of biomass-derived species because the use of water is inherently environmentally friendly. Cyclodehydration of C4 diols in aqueous solution was examined using a variety of water-tolerant solid acids including H-type zeolites (H-ZSM5, H-mordenite, H-beta), Amberlyst-15 ion-exchange resin, niobic acid and layered HNbMoO6. Cyclodehydration of 1,4-butanediol (HO-CH2CH2CH2CH2-OH) and erythritol (HO-CH2CH-OHCH-OHCH2-OH) proceeded on three of the Brønsted solid acids, HNbMoO6, H-ZSM5 and Amberlyst-15. Although HNbMoO6 showed moderate activity for 1,4-butanediol dehydration, it exhibited the highest activity for erythritol dehydration. Kinetic analysis indicated that 1,4-butanediol and erythritol dehydration over HNbMoO6 followed a Tamaru-type mechanism with two successive irreversible steps. A statistical mechanics analysis of the pre-exponential factor gave good agreement with experimental results, in which the pre-exponential factor for erythritol dehydration was much larger than that for 1,4-butanediol dehydration. Both erythritol and 1,4-butanediol could be intercalated in the interlayer spaces of the oxide. The expansion of the interlayer spaces for erythritol was, however, much larger than that for 1,4-butanediol. This improvement of accessibility is considered to be responsible for the higher reactivity of erythritol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...