Photochemical CO2 reduction using structurally controlled g-C3N4†
Abstract
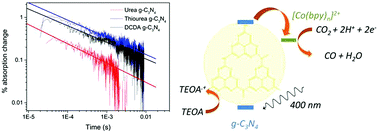
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) synthesised from a urea precursor is an excellent CO2 reduction photocatalyst using [Co(bpy)n]2+ as a co-catalyst. A five-fold increase in activity for the highly polymerised urea derived g-C3N4 is achieved compared to alternative precursors. Transient absorption, time-resolved and steady-state emission studies indicate that the enhanced activity is related to both an increased driving force for photoelectron transfer and a greater availability of photogenerated charges.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...