Biexponential photon antibunching: recombination kinetics within the Förster-cycle in DMSO†
Abstract
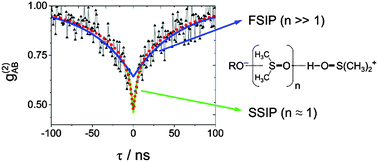
Time-resolved experiments with pulsed-laser excitation are the standard approach to map the dynamic evolution of excited states, but ground-state kinetics remain hidden or require pump–dump–probe schemes. Here, we exploit the so-called photon antibunching, a purely quantum-optical effect related to single molecule detection to assess the rate constants for a chemical reaction in the electronic ground state. The measurement of the second-order correlation function g(2), i.e. the evaluation of inter-photon arrival times, is applied to the reprotonation in a Förster-cycle. We find that the antibunching of three different photoacids in the aprotic solvent DMSO significantly differs from the behavior in water. The longer decay constant of the biexponential antibunching tl is linked to the bimolecular reprotonation kinetics of the fully separated ion-pair, independent of the acidic additives. The value of the corresponding bimolecular rate constant, kp = 4 × 109 M−1 s−1, indicates diffusion-controlled reprotonation. The analysis of tl also allows for the extraction of the separation yield of proton and the conjugated base after excitation and amounts to approximately 15%. The shorter time component ts is connected to the decay of the solvent-separated ion pair. The associated time constant for geminate reprotonation is approximately 3 ± 1 ns in agreement with independent tcspc experiments. These experiments verify that the transfer of quantum-optical experiments to problems in chemistry enables mechanistic conclusions which are hardly accessible by other methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...