The ultrafast reactions in the photochromic cycle of water-soluble fulgimide photoswitches†
Abstract
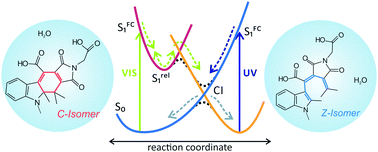
Photochromic switches are essential for the control and manipulation of nanoscale reactions and processes. The expansion of their application to aqueous environments depends strongly on the development of optimized water-soluble photoswitches. Here we present a femtosecond time-resolved investigation of the photochromic reactions (transition between the open and the closed form) of a water-soluble indolylfulgimide. We observe a pronounced effect of the protic nature of water as a solvent on the ultrafast ring-opening reaction. Typically, the excited state of the closed form has a larger dipole moment than the ground state, which leads to stabilization of the excited state in polar solvents and hence a lifetime (3 ps) longer than in non-polar solvents (2 ps). However, in water, despite the increased solvent polarity and the increased excited state dipole moment, the opposite trend for the excited state lifetime is observed (1.8 ps). This effect is caused by the opening of a new excited state deactivation pathway involving proton transfer reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...