The nature of chemical bonding in actinide and lanthanide ferrocyanides determined by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and density functional theory†
Abstract
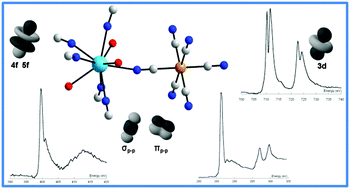
The electronic properties of actinide cations are of fundamental interest to describe intramolecular interactions and chemical bonding in the context of nuclear waste reprocessing or direct storage. The 5f and 6d orbitals are the first partially or totally vacant states in these elements, and the nature of the actinide ligand bonds is related to their ability to overlap with ligand orbitals. Because of its chemical and orbital selectivities, X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is an effective probe of actinide species frontier orbitals and for understanding actinide cation reactivity toward chelating ligands. The soft X-ray probes of the light elements provide better resolution than actinide L3-edges to obtain electronic information from the ligand. Thus coupling simulations to experimental soft X-ray spectral measurements and complementary quantum chemical calculations yields quantitative information on chemical bonding. In this study, soft X-ray XAS at the K-edges of C and N, and the L2,3-edges of Fe was used to investigate the electronic structures of the well-known ferrocyanide complexes K4FeII(CN)6, thorium hexacyanoferrate ThIVFeII(CN)6, and neodymium hexacyanoferrate KNdIIIFeII(CN)6. The soft X-ray spectra were simulated based on quantum chemical calculations. Our results highlight the orbital overlapping effects and atomic effective charges in the FeII(CN)6 building block. In addition to providing a detailed description of the electronic structure of the ferrocyanide complex (K4FeII(CN)6), the results strongly contribute to confirming the actinide 5f and 6d orbital oddity in comparison to lanthanide 4f and 5d.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...