In situ monitoring the role of citrate in chemical bath deposition of PbS thin films
Abstract
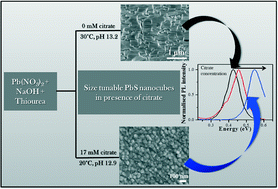
Trisodium citrate (citrate) has been commonly used as a co-complexing agent during chemical bath deposition to improve film quality and control grain size, yet its precise role has not been elucidated to date. In this study, we have focused on the role of citrate in chemically deposited PbS thin films. Citrate effectively complexes the lead cation in solution thereby decreasing growth rate and inducing growth in the cluster mechanism. This was monitored in real time using laser light-scattering and UV-vis absorption spectroscopy which quantitatively confirmed the retarded PbS formation in the cluster mechanism in the presence of citrate. Nanocrystalline PbS films formed in the presence of citrate show quantum confinement effects with blue shifted optical properties compared to the bulk, adding an important path for controlling film properties towards future infrared optoelectronic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...