Abstract
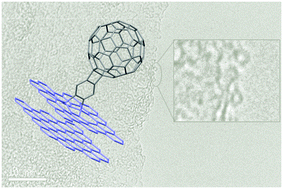
The synthesis of a [60]fullerene-benzyne building block and its further chemical cycloaddition reaction with graphene has resulted in a new all-carbon hybrid material which has been characterized by TGA, FTIR and Raman spectroscopies, XPS as well as AFM and TEM. Based on computational studies, the formation of both [2+2] and [4+2] cycloadducts on the graphene surface is feasible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...