MoS2/graphene cathodes for reversibly storing Mg2+ and Mg2+/Li+ in rechargeable magnesium-anode batteries†
Abstract
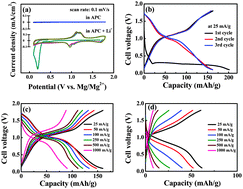
Commercial micron-scale low-cost MoS2 is subjected to an electrochemically derived 2H-to-1T phase transformation, which makes it capable of reversibly storing Mg2+/Li+ and Mg2+ in all-phenyl-complex (APC) electrolytes with and without Li+, respectively. The MoS2/graphene composite shows a high capacity (225 mA h g−1) and great cyclic stability in the Li+-containing APC electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...