Nitric oxide-generating l-cysteine-grafted graphene film as a blood-contacting biomaterial†
Abstract
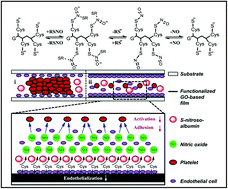
By using polyethylenimine molecules as the linker, L-cysteine was immobilized onto graphene nanosheets, endowing the biocompatible L-cysteine-functionalized graphene film with the ability for catalytic decomposition of exogenous or endogenous donors to generate nitric oxide, and thus inhibiting the platelet activation and aggregation and reducing platelet adhesion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...