A selective and sensitive pre-column derivatization HPLC method for the trace analysis of genotoxic impurity hydroxylamine in active pharmaceutical ingredients
Abstract
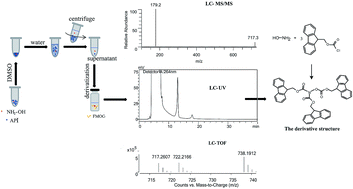
A simple and robust high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method for the trace analysis of genotoxic impurity hydroxylamine in Vorinostat and Zileuton, two active pharmaceutical ingredients, is described. This method was based on a conventional pre-column derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate using UV detection. In order to avoid the degradation of the API during derivatization, an innovative pretreatment utilizing precipitation prior to derivatization is proposed, and this simple and robust method demonstrates reliable recovery and excellent anti-interference capability. To minimize and stabilize the competition, optimization of the derivatization was conducted under both hydrous and anhydrous conditions in terms of reaction time, temperature, concentrations of FMOC-Cl, sodium borate, alkaloid species and the corresponding volumes, and pH values. To compare the reactivity, all of the derivatives of hydroxylamine and APIs were identified by LC-TOF/MS and LC-MS/MS. The optimized analytical method was fully validated, which demonstrated it to be sensitive, repeatable, accurate and convenient for routine quality control. The result suggested that the trace level of genotoxic impurity hydroxylamine in APIs could be effectively determined by this classical and robust HPLC method, and degradation in the procedure and competition in derivatization issues have been resolved successfully.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...