The selective detection of galactose based on boronic acid functionalized fluorescent carbon dots†
Abstract
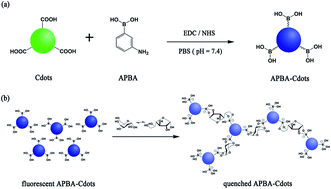
In this paper, we presented a galactose biosensing system based on boronic acid functionalized carbon dots (APBA-Cdots) as the fluorescent probe. Carbon dots were directly synthesized by chemical oxidation with strong acids, and then they were linked to m-aminophenylboronic acid to form the APBA-Cdot fluorescent probe. Boronic acid groups on APBA-Cdot surfaces could covalently react with cis-diol units in galactose to form five- or six-membered cyclic esters. Compared with the close isomeric cousins of galactose such as fructose and glucose, galactose molecules possess more cis-conformational diol units in both pyranose and furanose forms, and as a result, they could selectively lead to the assembly and fluorescence quenching of APBA-Cdots. The fluorescence intensity linearly decreased with increase of galactose concentration in the range of 0 to 500 μM, and a detection limit as low as 6.2 μM was achieved. The proposed sensing system has been successfully used for the assay of galactose in human urine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...