Electrolysis-induced fast activation of the ABTS reagent for an antioxidant capacity assay
Abstract
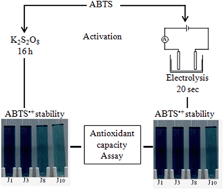
An improved TEAC (Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity) analytical procedure to evaluate the in vitro antioxidant capacity of some radical scavengers, including copper proteins (i.e. hemocyanin, ceruloplasmin or diamine oxidase) and some copper complexes (i.e. serine2–copper), is described. The TEAC method consists in measuring the reduction of the 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt radical monocation (ABTS˙+) with a decoloration induced by the scavenger to be analyzed. Several disadvantages, such as a particularly long time (about 16 h) for the activation of ABTS with potassium persulfate (free radical initiator), justify the need to improve this operatory mode. Consequently, we propose a new procedure consisting in a rapid activation of ABTS by electrolysis in about 20 s instead of 16 hours as required by the activation with potassium persulfate. Furthermore, the ABTS activation by electrolysis provides an improved reagent stability for 7–8 days whereas the stability in the case of the classical method is limited to 3 days. The fast assay was compared with the classical activation with potassium persulfate as a method of reference to activate ABTS and the results were expressed in equivalents of Trolox (standard reference scavenger). A good linearity of the answer in terms of Trolox amounts has been obtained with the fast assay, as with the classical method. Therefore, the fast assay seems compatible with the classical method, with the only difference and advantage that it is much faster and easier to operate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...