Determination of tetraiodo-l-thyronine in human serum by competitive indirect chemiluminescence immunoassay†
Abstract
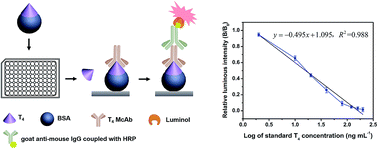
Based on the monoclonal antibodies against 3,3′,5,5′-tetraiodo-L-thyronine (T4), a competitive indirect chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) used for the quantitative determination of total T4 in human serum was established. The relevant results indicated that the determined coating antigen concentration was 2.7 μg mL−1 and the CLEIA titer of ascites was 1 : 8.0 × 104. The standard curve was y = −0.495x + 1.095, with a coefficient of determination, R2 = 0.988, and the derived half inhibition concentration (IC50) of T4 was 16.0 ng mL−1. The system detection limit was 9.23 ng mL−1. The mean inter- and intra-assay variations were 5.89% and 4.02%, respectively. The detected data of total T4 in human serum from seven patients by this method exhibited significant correlation with reported clinical data, suggesting that this CLEIA method could be applicable to the clinical diagnosis of thyroid gland disease.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...