Facile interfacial charge transfer across hole doped cobalt-based MOFs/TiO2 nano-hybrids making MOFs light harvesting active layers in solar cells†
Abstract
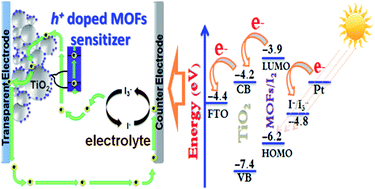
Efficient separation of charges and their mobility are key challenges in metal–organic-framework (MOF) based devices. In the present study, thin films of cobalt-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are synthesized using a layer-by-layer technique, and their electrical/optoelectronic properties are studied. The as-prepared MOF films show electrically insulating behavior, which after hole doping demonstrate p-type conduction behaviour. The measured HOMO–LUMO energy states of the MOF films are found to be well matched for sensitizing TiO2, and the photoluminescence quenching experiment demonstrates a facile photoelectron transfer path from the doped frameworks to TiO2. Consequently, the doped MOFs are employed successfully as light harvesting and charge transporting active layers in a fully devised TiO2-based solar cell. Two different organic ligands viz., benzene dicarboxylic acid and naphthalenedicarboxylic acid are used to synthesize two kinds of Co–MOFs having different geometrical dimensions of unit cells and pores, and their influence on hole doping and charge transportation is studied. Under optimized conditions, the Co–MOF based device demonstrates a solar-to-electric energy conversion efficiency of 1.12% with a short circuit current of 2.56 mA cm−2, showing promising future prospects of the application of Co–MOFs in photovoltaic devices. Further, the photovoltaic performance of the Co–MOF based device is comparatively studied with that of the previously reported Cu–MOF and Ru–MOF based similar devices, and the influence of different metal centers of MOFs on their light harvesting performance is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...