Anion-effects on electrochemical properties of ionic liquid electrolytes for rechargeable aluminum batteries
Abstract
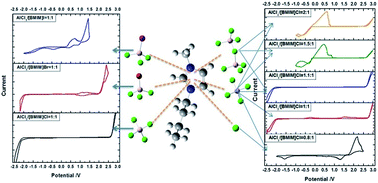
A rechargeable aluminum battery is considered as a promising battery system used in energy storage devices, due to its natural abundance and high capacity. However, fabrication of this battery working at room temperature did not succeed until haloaluminate containing ionic liquids were used as electrolytes. Therefore, anions are expected to have a great effect on performance of rechargeable aluminum batteries. For a complete understanding of the anion-effect, haloaluminate containing ionic liquids prepared with different halogenated imidazole salt and AlCl3/imidazolium chloride mole ratios are studied. The electrochemical window is found to narrow with reducibility of halide ions, which is confirmed by calculation results using the density functional theory (DFT) method. For ionic liquids at different mole ratios, the coexistence of different chloroaluminate anions (Cl−, AlCl4−, Al2Cl7−) is found. When used as an electrolyte in a rechargeable aluminum battery with a V2O5 nanowire cathode, the AlCl3/[BMIM]Cl ionic liquid with the mole ratio of 1.1 : 1 shows the best performance. The as-assembled cell exhibits a high discharge voltage platform (1 V) and capacity (288 mA h g−1) at the first cycle. Concentration of Al2Cl7− is considered as a key factor in chloroaluminate ionic liquids when used as electrolytes. Furthermore, a slight corrosion is found on the surface of Al metal foil immersed in an AlCl3/[BMIM]Cl = 1.1 : 1 ionic liquid for 24 h, which may help remove the oxide film on the Al metal foil, so as to improve the charge/discharge performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...