Low voltage actuator using ionic polymer metal nanocomposites based on a miscible polymer blend†
Abstract
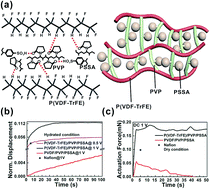
Bio-compatible actuators are required to exhibit a large actuation displacement and force at a low voltage for various applications in liquid environments, including swimming robots, biomedical catheters, biomimetic sensory-actuators, and drug delivery micro-pumps. Recently, ionic polymer metal nanocomposites (IPMNCs) based on Nafion have been widely used for bio-compatible actuators; however, they have been demonstrated to operate only at high voltages in the range of 2 to 5 V, resulting in water hydrolysis problems which are accompanied by a degradation of actuation performance. Here, we show that IPMNC actuators based on a poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) [P(VDF-TrFE)]/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)/polystyrene sulfonic acid (PSSA) polymer blend membrane can exhibit a large actuation displacement and force at a low voltage of 1 V. Due to the ferroelectric nature of P(VDF-TrFE), the large dipole moment of P(VDF-TrFE) can cause strong intermolecular bonding, causing the P(VDF-TrFE)/PVP/PSSA blend membrane to be miscible. We found that the P(VDF-TrFE)/PVP/PSSA blend membrane with a blending ratio of 30/15/55 can produce the highest proton conductivity (0.0065 S cm−1) and ion exchange capacity (2.95 meq g−1) as compared to those of the commercial Nafion membrane, due to its miscible nature. Our IPMNC exhibits both an enhanced actuation displacement and force by up to 2 times in comparison with those of the IPMNC based on the commercial Nafion-based ionic membrane. Our P(VDF-TrFE)/PVP/PSSA IPMNC shows a stable actuation performance for up to 2200 cycles in hydrated conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...