Constructing the optimal conductive network in MnO-based nanohybrids as high-rate and long-life anode materials for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
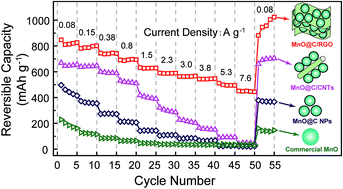
Among the transition metal oxides as anode materials for lithium ion batteries (LIBs), the MnO material should be the most promising one due to its many merits mainly relatively low voltage hysteresis. However, it still suffers from inferior rate capabilities and poor cycle life arising from kinetic limitations, drastic volume changes and severe agglomeration of active MnO particulates during cycling. In this paper, by integrating the typical strategies of improving the electrochemical properties of transition metal oxides, we had rationally designed and successfully prepared one superior MnO-based nanohybrid (MnO@C/RGO), in which carbon-coated MnO nanoparticles (MnO@C NPs) were electrically connected by three-dimensional conductive networks composed of flexible graphene nanosheets. Electrochemical tests demonstrated that, the MnO@C/RGO nanohybrid not only showed the best Li storage performance in comparison with the commercial MnO material, MnO@C NPs and carbon nanotube enhanced MnO@C NPs, but also exhibited much improved electrochemical properties compared with most of the previously reported MnO-based materials. The superior electrochemical properties of the MnO@C/RGO nanohybrid included a high specific capacity (up to 847 mA h g−1 at 80 mA g−1), excellent high-rate capabilities (for example, delivering 451 mA h g−1 at a very high current density of 7.6 A g−1) and long cycle life (800 cycles without capacity decay). More importantly, for the first time, we had achieved the discharging/charging of MnO-based materials without capacity increase even after 500 cycles by adjusting the voltage range, making the MnO@C/RGO nanohybrid more possible to be a really practical anode material for LIBs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...