Design of a Kagome lattice from soft anisotropic particles†
Abstract
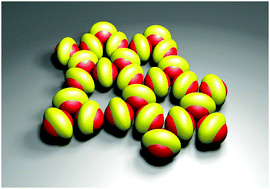
We present a simple model of triblock Janus particles based on discoidal building blocks, which can form energetically stabilized Kagome structures. We find ‘magic number’ global minima in small clusters whenever particle numbers are compatible with a perfect Kagome structure, without constraining the accessible three-dimensional configuration space. The preference for planar structures with two bonds per patch among all other possible minima on the landscape is enhanced when sedimentation forces are included. For the building blocks in question, structures containing three bonds per patch become progressively higher in energy compared to Kagome structures as sedimentation forces increase. Rearrangements between competing structures, as well as ring formation mechanisms are characterised and found to be highly cooperative.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...