A new quinoxaline-containing peptide induces apoptosis in cancer cells by autophagy modulation†
Abstract
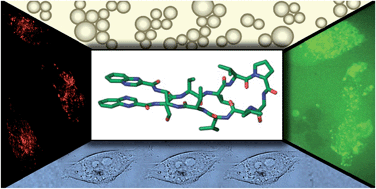
The synthesis of a new small library of quinoxaline-containing peptides is described. After cytotoxic evaluation in four human cancer cell lines, as well as detailed biological studies, it was found that the most active compound, RZ2, promotes the formation of acidic compartments, where it accumulates, blocking the progression of autophagy. Further disruption of the mitochondrial membrane potential and an increase in mitochondrial ROS was observed, causing cells to undergo apoptosis. Given its cytotoxic activity and protease-resistant features, RZ2 could be a potential drug candidate for cancer treatment and provide a basis for future research into the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis and its relevance in cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...