Controlled synthesis of Zn(1−1.5x)FexS nanoparticles via a microwave route and their photocatalytic properties†
Abstract
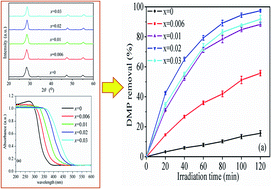
Fe-doped ZnS photocatalysts synthesized by a conventional hydrothermal method usually have poor crystallinity and low photocatalytic activity. In this study, the Zn(1−1.5x)FexS particles were first directly synthesized by the microwave irradiation method without additional heat treatments. The prepared Zn(1−1.5x)FexS catalysts were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-Vis absorption spectra, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analyzer, etc. The characterization results show that the morphology and physico-chemical properties of samples are changed depending on the ratio of Fe and Zn. The absorption edges of Zn(1−1.5x)FexS were red-shifted as the value of x decreased. The band gaps were estimated to be from 2.74 to 3.64 eV from the onset of the UV-Vis absorption edges. The results indicated that the photocatalyst of Zn0.97Fe0.02S has the highest photocatalytic activity of dimethyl phthalate (DMP) with a removal of 97.5%. In addition, the crystallite size, band gap and structure for the Zn(1−1.5x)FexS samples have a strong influence on the degradation of DMP from wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...