The effect of nanonization on poorly water soluble glibenclamide using a liquid anti-solvent precipitation technique: aqueous solubility, in vitro and in vivo study†
Abstract
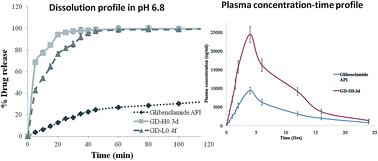
The aim of the present research was to improve the aqueous solubility and oral bioavailability of glibenclamide (GLB), a BCS class-II drug. A GLB nanosuspension (NS) was prepared using a liquid anti-solvent (LAS) precipitation technique and stabilized using HPMC K15M and lactose. Different in-process variables which directly affect the precipitated particle size have been thoroughly studied and optimized. The effect of a cryoprotective agent which could prevent agglomeration during lyophilisation was investigated. The optimal formulations of GD-H0.3d and GD-H0.4f exhibited a size range of 168.6 and 342.2 nm respectively and did not show any interaction when screened for incompatibility using FT-IR and DSC, but exhibited a decrease in crystallinity. The prepared GLB NPs exhibited superior aqueous solubility and dissolution when compared to pure GLB. The oral bioavailability of optimized formulations was found to exhibit 2.59, 1.67, 1.19, 2.50 and 2.40 folds of increment with respect to Cmax, Kel (h−1), t1/2, AUC0–24 h and AUC0–∞ for GD-0.3d in contrast to pure GLB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...