Fabrication and evaluation of protein imprinted polymer based on magnetic halloysite nanotubes
Abstract
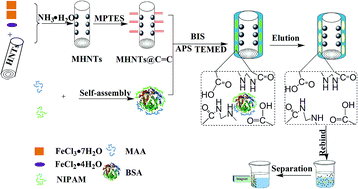
A novel protein imprinted polymer, which combined the surface imprinting technology and magnetic halloysite nanotubes (MHNTs), was prepared for selective separation of a template protein. In this work, MHNTs were synthesized through the coprecipitation method based on encapsulation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in halloysite nanotubes. The surface of the MHNTs was modified with vinyl groups through reaction with 3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl trimethoxysilane. Subsequently, the modified MHNTs were used as a support, N-isopropylacrylamide and methacrylic acid as bifunctional monomers, N,N′-methylene bisacrylamide as the crosslinking agent, and ammonium persulphate and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine as initiators. The resulting polymer was named MHNTs@BSA-MIP, which was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and vibrating sample magnetometry. The MHNTs@BSA-MIP exhibited high adsorption (48.4 mg g−1), good selectivity, rapid kinetic binding (45 min), fast magnetic separation (10 s), and favorable reproducibility (relative standard deviation <8% for batch-to-batch evaluation). The prepared MHNTs@BSA-MIP is suitable for separation and provides a significant reference for other proteins in proteomics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...