Template size matched film thickness for effectively in situ surface imprinting: a model study of glycoprotein imprints
Abstract
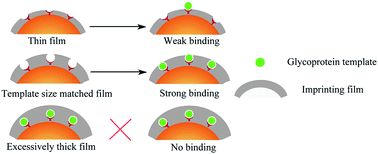
Precisely controlling the material structure is a high requirement for biological target imprinting. In situ surface imprinting immobilized templates can offer thin-film molecular imprints containing site-directed binding sites on substrates, and therefore is appropriate for biological targets. However, the correlation between the required film thickness for superior imprinting effect and the bulk structure of biological template is not clearly understood. Here we use a series of glycoprotein imprinted films as a model to give a semi-quantitative description for their correlation. Glycoproteins with distinguished molecular sizes including ribonuclease B, glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase were used as templates. Covalently immobilizing glycoproteins was achieved by using m-aminophenylboronic acid modified SiO2 or Fe3O4 surface. Dopamine was polymerized onto this surface for glycoprotein imprinting. Varying polymerization time provided a series of thickness tunable imprinting films in nanometer-scale. The binding isotherm study for each glycoprotein imprints with different film thickness was performed. The optimal film thickness for the highest binding capacities and imprinting factors shows a positive correlation with its template size. The each optimized glycoprotein imprints can recognize their template in a simple or complex environment. These results suggest that the thickness of imprinted film should be tailored for matching the geometric size of fixed templates, and reveal the substantial influence of template structure on imprints design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...