Modelling the effects of surfactant loading level on the sorption of organic contaminants on organoclays†
Abstract
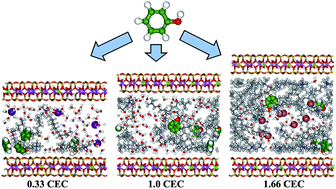
Organoclays can effectively uptake organic contaminants (OCs) from water media, but the sorption mechanisms are not fully established yet, because of the lack of recognition of interlayer structure of organoclays. To unravel this complex behavior, we have examined the effects of surfactant loading on the interlayer structure and sorption behaviors of organoclays using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The sorption behavior of phenol on three cetyltrimethylammonium intercalated montmorillonite (CTMA-Mt) with CTMA loading levels of 0.33, 1.0, and 1.66 times of the Mt's cation exchange capacity (CEC), was studied. The results demonstrated that CTMA aggregates were the main sorption domains for phenol molecules, consistent with a partition process. The interlayer structure of CTMA-Mt influences the sorption affinity of phenol. CTMA aggregates increased in size with increasing loading level, creating larger sorption domains for phenol uptake. On the other hand, high CTMA loading level decreased the sorption affinity of CTMA-Mt (with 1.66 CEC loading) toward phenol by increasing the packing density and cohesive characteristic of the aggregates. In addition, the siloxane surfaces of Mt and the hydrated inorganic ions (Ca2+ or Br−) showed specific interactions with phenol molecules by forming H-bond. The oxygen atoms on siloxane surface and water molecules around Br− serve as H-bond acceptor while water molecules around Ca2+ serve as H-bond donor, corresponding to polyparameter linear free energy relationships (pp-LFERs) results. The modelling results correlate well with the experimental findings, and further reveal that the sorption affinity strongly depends on the size and packing density of surfactant aggregates. In addition, H-bond interactions should be considered as well in the sorption of OCs containing particular groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...