Linear solvent structure-polymer solubility and solvation energy relationships to study conductive polymer/carbon nanotube composite solutions†
Abstract
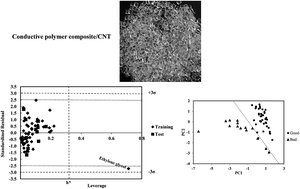
The solvation and solvent selectivity of polymer composites in different solvents is an important subject in colloid and polymer chemistry. Two multiparameter linear models based on theoretical and empirical parameters were constructed and validated for 59 and 54 solvents, respectively, to predict the relative energy difference (RED) of the solvents and a conductive polymer composite containing carbon nanotube. In addition to the excellent external prediction ability, models 1 (QSPR) and 2 (LSER) covered 87% and 93% of cross-validated variance, respectively. Different statistical methods were applied to test and validate the models. From the descriptive view, it was shown by model 1 that the compactness of solvent structure, mass and polar interactions are important in the resistance of the polymer and its RED in the desired solvent. In addition to the Hildebrand solubility parameter, acidity of the solvent and hydrogen bonding interactions have a direct relationship with RED. Both the models confirmed the moderate and complex effect of polar interactions in the solvation of desired polymer composites in different solvents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...