Role of pentahedrally coordinated titanium in titanium silicalite-1 in propene epoxidation†
Abstract
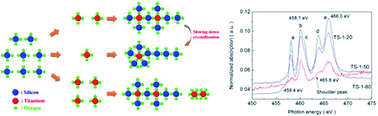
Two titanium silicalite-1 samples with different crystal sizes were synthesized in the tetrapropylammonium bromide (TPABr) and tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) hydrothermal systems. The small-crystal TS-1 with a size of 600 nm was then treated with different organic bases. These TS-1 samples were evaluated in the epoxidation of propene, and characterized by ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance (UV-vis), X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and Raman spectroscopies. The Ti L-edge absorption spectra show that a new Ti species, pentahedrally coordinated Ti, appears in some of the samples. This pentahedrally coordinated Ti species is correlated with the catalytic oxidation activity of TS-1, closely. Tetrahedrally coordinated Ti in TS-1 is the primary active center for selective oxidation reactions, but the existence of a small amount of pentahedrally coordinated Ti can further improve the catalytic activity. A high molar ratio of Si/Ti (n(Si/Ti)) in the synthesis process (n(Si/Ti) = 92.78) was beneficial for the generation of pentahedrally coordinated Ti. The improved catalytic activity of the TPAOH treated TS-1 is mainly due to the increasing amount of pentahedrally coordinated Ti, besides the elimination of diffusion limitation. Slowing down the crystallization rate can also increase the content of pentahedrally coordinated Ti.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...