Modulated photophysics of an anthracene-based fluorophore within bile-salt aggregates: the effect of the ionic strength of the medium on the aggregation behavior†
Abstract
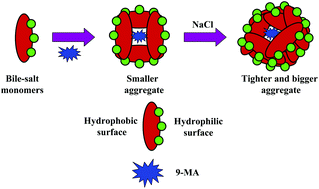
In this article, the binding interactions of a promising chloride channel blocker 9-methyl anthroate (9-MA) with a series of bile-salt aggregates of varying hydrophobicity have been thoroughly demonstrated. The altered photophysical properties of the fluorescent probe within the concerned microheterogeneous environments have been exploited spectroscopically to assess the communication between the aggregates and the guest. The contrived hydrophobic environment provided by the aggregates appreciably diminishes the water-assisted non-radiative decay channels and thus extends the fluorescence lifetime and the rotational relaxation time of the probe. NaDC aggregates, being more rigid and hydrophobic, provide a better protection to the bound guest from the external influence which is apparent from a much longer fluorescence lifetime and rotational correlation time for the encapsulated probe in NaDC aggregates compared to those in NaC and NaTC aggregates, as is further validated by fluorescence quenching experiments. Salt induced alterations of the binding behavior of the probe with the bile-salt aggregates have also been evaluated via fluorimetric studies, which conclude larger and tighter aggregate formation resulting in a superior degree of rigidity imposed on the aggregate-bound probe at high ionic strength of the medium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...