Aliphatic acid-conjugated antimicrobial peptides – potential agents with anti-tumor, multidrug resistance-reversing activity and enhanced stability
Abstract
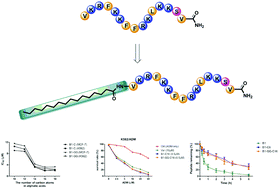
Compared with traditional therapeutics, antimicrobial peptides as novel anti-tumor agents have prominent advantages of higher specificity and circumvention of multi-drug resistance. In a previous study, we found that B1, an antimicrobial peptide derived from Cathelicidin-BF15, presented specific anti-tumor activity against several tumor cells. Since aliphatic chain-conjugated peptides have shown ameliorative activity and stability, we conjugated aliphatic acids with different lengths to the amino terminal of B1. All the conjugated peptides exhibited improved anti-tumor activity over B1. Further investigations revealed that the peptides were capable of disrupting the cell membrane, stimulating cytochrome c release into the cytosol, which results in apoptosis. The peptides also acted against multidrug resistant cells and had multidrug resistance-reversing effects. Additionally, conjugation of aliphatic acid enhanced the peptide stability in plasma. In summary, aliphatic acid-modified peptides might be promising anti-tumor agents in the future.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...