Aspartic acid based nucleoside phosphoramidate prodrugs as potent inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication†
Abstract
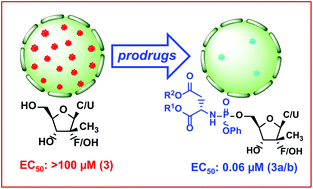
In view of a persistent threat to mankind, the development of nucleotide-based prodrugs against hepatitis C virus (HCV) is considered as a constant effort in many medicinal chemistry groups. In an attempt to identify novel nucleoside phosphoramidate analogues for improving the anti-HCV activity, we have explored, for the first time, aspartic acid (Asp) and iminodiacetic acid (IDA) esters as amidate counterparts by considering three 2′-C-methyl containing nucleosides, 2′-C-Me-cytidine, 2′-C-Me-uridine and 2′-C-Me-2′-fluoro-uridine. Synthesis of these analogues required protection for the vicinal diol functionality of the sugar moiety and the amino group of the cytidine nucleoside to regioselectively perform phosphorylation reaction at the 5′-hydroxyl group. Anti-HCV data demonstrate that the Asp-based phosphoramidates are ∼550 fold more potent than the parent nucleosides. The inhibitory activity of the Asp-ProTides was higher than the Ala-ProTides, suggesting that Asp would be a potential amino acid candidate to be considered for developing novel antiviral prodrugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...