Sulfonate derived phosphoramidates as active intermediates in the enzymatic primer-extension of DNA†
Abstract
Novel unnatural 5′-phosphoramidate nucleosides, capable of being processed as substrates by DNA polymerases for multiple nucleotide incorporations, have been designed. The mimics feature metabolites such as taurine and a broad range of aliphatic sulfonates coupled through a P–N bond to the 5′-phosphate position of deoxynucleotides, to allow binding interactions in the enzyme active site. The utility of all of the analogues as pyrophosphate mimics was demonstrated for the chain elongation of DNA, using both thermophilic and mesophilic microbial polymerases.
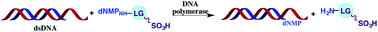

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...