Unraveling the contributions of hydrogen-bonding interactions to the activity of native and non-native ligands in the quorum-sensing receptor LasR†
Abstract
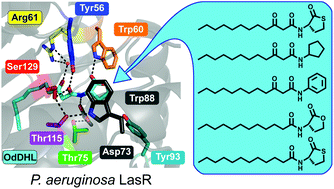
Quorum sensing (QS) via the synthesis and detection of N-acyl L-homoserine lactone (AHL) signals regulates important pathogenic and mutualistic phenotypes in many bacteria. Over the past two decades, the development of non-native molecules that modulate this cell–cell signaling process has become an active area of research. The majority of these compounds were designed to block binding of the native AHL signal to its cognate LuxR-type receptor, and much effort has focused on LasR in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Despite a small set of reported LasR structural data, it remains unclear which polar interactions are most important for either (i) activation of the LasR receptor by its native AHL signal, N-(3-oxo)-dodecanoyl L-homoserine lactone (OdDHL), or (ii) activation or inhibition of LasR by related AHL analogs. Herein, we report our investigations into the activity of OdDHL and five synthetic analogs in wild-type LasR and in nine LasR mutants with modifications to key polar residues in their ligand binding sites. Our results allowed us to rank, for the first time, the relative importance of each LasR:OdDHL hydrogen bond for LasR activation and provide strong evidence for the five synthetic ligands binding LasR in a very similar orientation as OdDHL. By delineating the specific molecular interactions that are important for LasR modulation by AHLs, these findings should aid in the design of new synthetic modulators of LasR (and homologous LuxR-type receptors) with improved potencies and selectivities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...