Modeling nanoparticle wrapping or translocation in bilayer membranes
Abstract
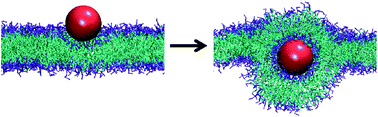
The spontaneous wrapping of nanoparticles by membranes is of increasing interest as nanoparticles become more prevalent in consumer products and hence more likely to enter the human body. We introduce a simulations-based tool that can be used to visualize the molecular level interaction between nanoparticles and bilayer membranes. By combining LIME, an intermediate resolution, implicit solvent model for phospholipids, with discontinuous molecular dynamics (DMD), we are able to simulate the wrapping or embedding of nanoparticles by 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) bilayer membranes. Simulations of hydrophilic nanoparticles with diameters from 10 Å to 250 Å show that hydrophilic nanoparticles with diameters greater than 20 Å become wrapped while the nanoparticle with a diameter of 10 Å does not. Instead this smaller particle became embedded in the bilayer surface where it can interact with the hydrophilic head groups of the lipid molecules. We also investigate the interaction between a DPPC bilayer and hydrophobic nanoparticles with diameters 10 Å to 40 Å. These nanoparticles do not undergo the wrapping process; instead they directly penetrate the membrane and embed themselves within the inner hydrophobic core of the bilayers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...